Wiring Harnesses and Conduits
Mini Project Create Wiring Harnesses
In this project, you will use conduit to create clean and organized wiring harnesses to connect the components of your system together. In this project, you will be using flexible conduit to make a clean wiring harness to connect the Arduino to Distance Sensor.

Find the following components in your kit:
-
 Form Core E-Panel with Cutouts
Form Core E-Panel with Cutouts
-
 Arduino Uno
Arduino Uno
-
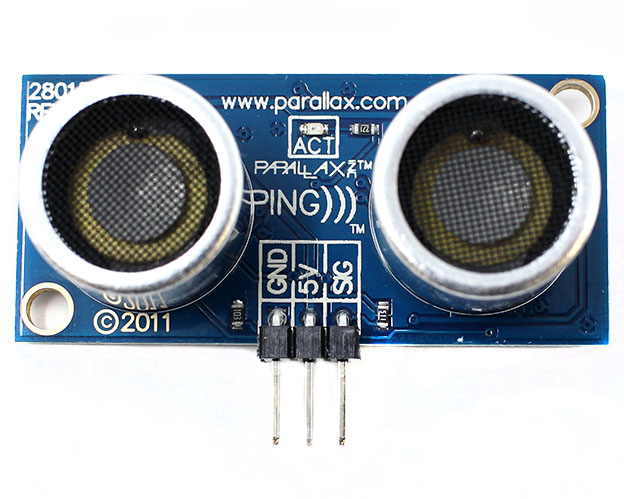 Distance Sensor
Distance Sensor
-
 Flexible Conduit
Flexible Conduit
-
 Wire Cutters
Wire Cutters
-
 3 Wires (red, black, and white) of 22 AWG 5 pin wire
3 Wires (red, black, and white) of 22 AWG 5 pin wire
-
 Male Header Pins
Male Header Pins
-
 Header Pin Crimper
Header Pin Crimper
-
 Zip Ties
Zip Ties

Using zip ties, attach the Arduino to the board by poking holes in the provided screw holes, and pushing the zip tie down one hole, and up the other side. Repeat this process with the other set of holes.

Using zip ties, attach the Distance Sensor to the board. You can do this by wrapping the zip tie between the two cylinders of the Distance Sensor.

Measure the distance of the wiring that you will need to connect the Arduino to the Distance Sensor. Make sure to give an extra inch of clearance for when you cut and crimp the header pins on the wires.
Cut that amount of wire.

Take the red, black, and white wires, and attach male header pins to the end of them. Then take the other end of the red, black, and white wires, and attach female header pins to the end of them.
For a refresher on how to attach male header pins to your wire, complete the following steps.
To begin attaching and crimping spade connectors, you will need the following:
-
 22 AWG Wire
22 AWG Wire
-
 Wire Cutter/Stripper
Wire Cutter/Stripper
-
 Header Pin Crimper
Header Pin Crimper
-
 Male or Female Header Crimps
Male or Female Header Crimps
-
 Header pin housings or shells
Header pin housings or shells
-
 Needle nose pliers or Wire Cutter / Stripper
Needle nose pliers or Wire Cutter / Stripper
You may want to have extra crimps and wires. These crimps are small, require a special crimping tool, precise techniques and practice to create a proper crimp.
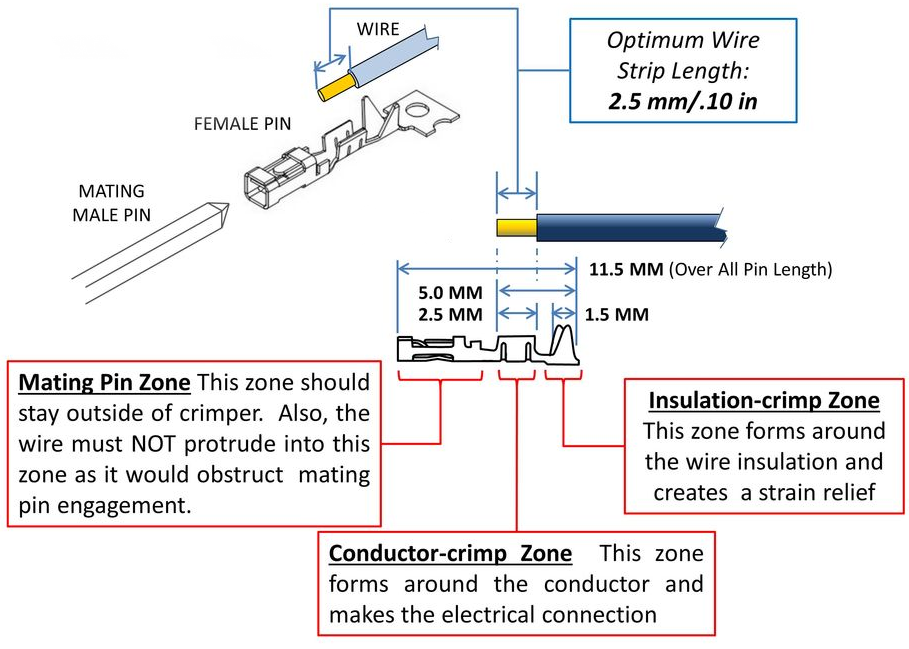
Header pin crimps are made up of three distinct portions: The mating pin zone is the portion of the crimp that interfaces with the component that you are connecting to. The other two portions interface with the wire. There is the conductor crimp zone which is the portion of the cimp that forms around the conductor and makes the electrical connection. The final part is the insulation crimp zone, where this part of the crimp forms around the wire’s insulation. This further securies the wire and creates a strain release. Both male and female header pins are crimped using the same process.
Cut a piece of the wire to the needed length and separate the number of wire you need from the .
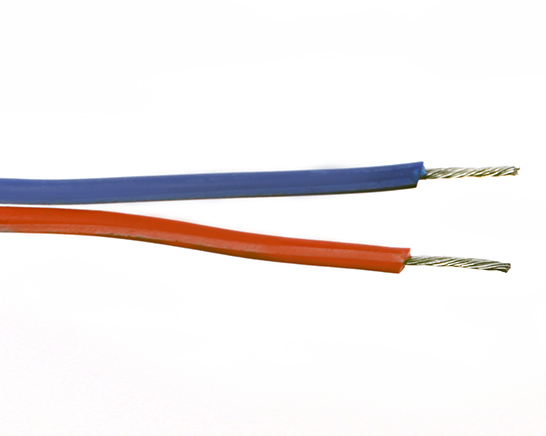
Strip the ends of the wire so that 0.10 in or 2.5 mm of wire is exposed. It may be easier to strip the wires longer and trim the exposed wires to 0.10 in or 2.5 mm.
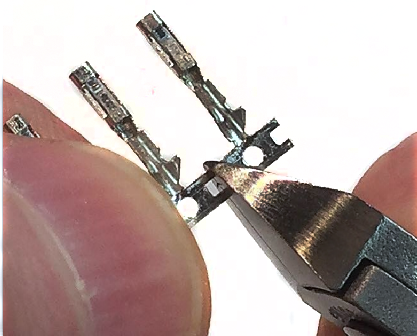
Cut off the male or female pin off of their connector strips. Keep the metal tab connected to the crimp, it will be used to align the crimp into the header pin crimper.

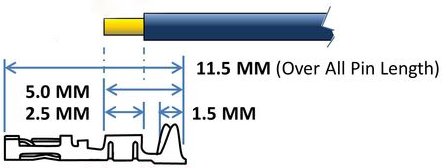
Place the wire into the crimp. Make sure the exposed wire is not in the mating pin zone.
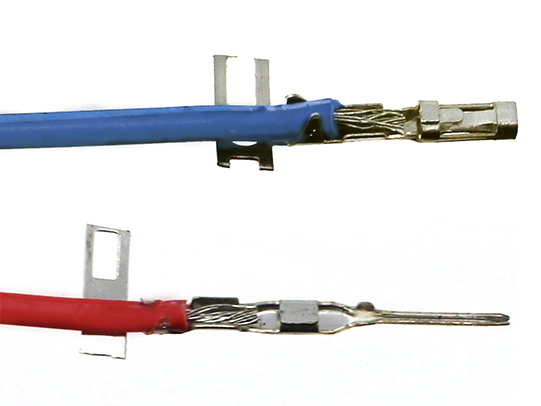
To give your crimp a better chance to be successful use your wire cutters or needle nose pliers to start to fold over the tabs on the insulation crimp zone.
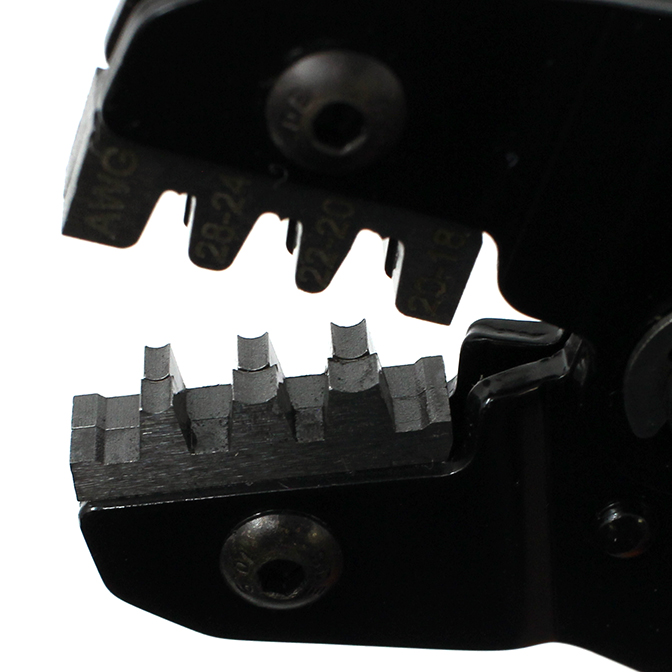

The recommended crimper has 2 different crimping areas the larger anvil crimps the insulation zone while the smaller anvil crimps the conductor zone. Make sure to line up the zones correctly or the crimp will not crimp properly.
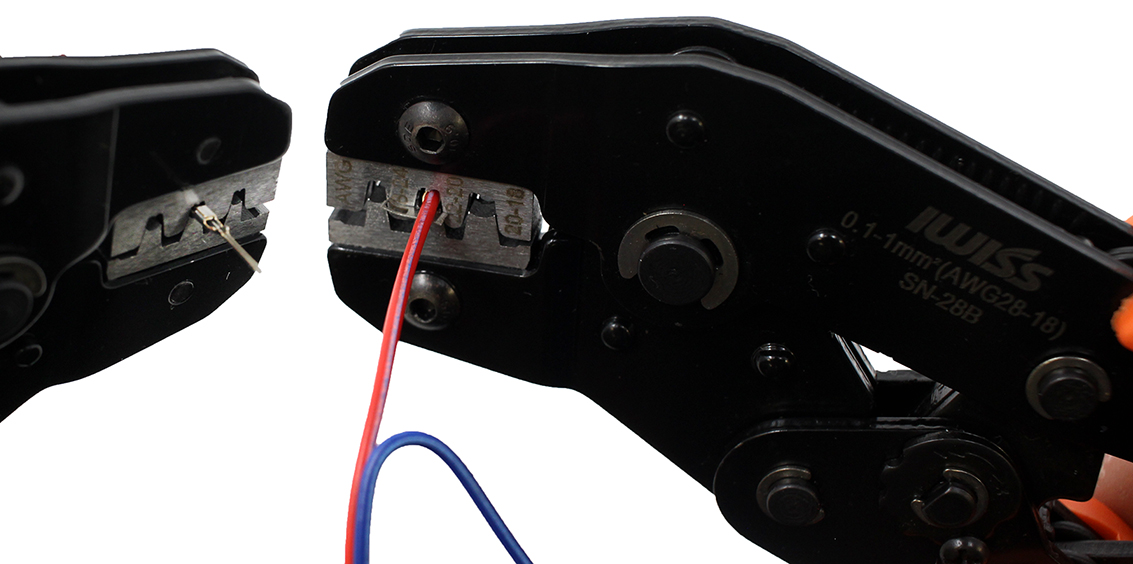
Use the crimping tool to crimp the conductor crimp zone and the insulation crimp zone. Make sure the Mating pin zone is extended completely out of the crimping tool. If you crimp this part it will deform and will not function
After crimping, if you inspect the connection and see that the crimped parts are not fully compressed onto the wire you may want to crimp the connection a second time.
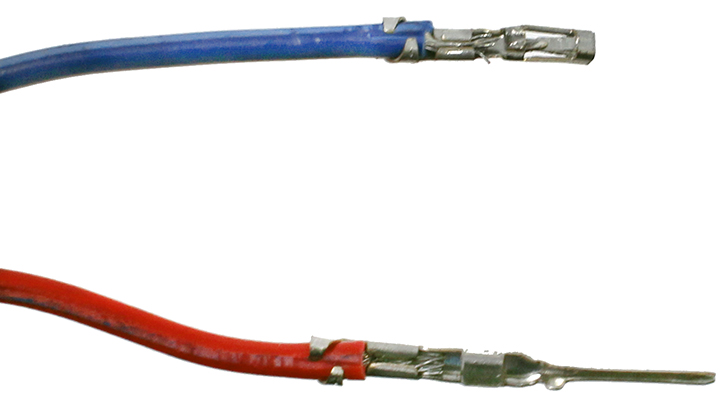
Once the crimp is successfully attached to the wire you can remove the metal carrier strip by bending or cutting it off. After removing that, the crimp is ready to be placed into the plastic housing.
The plastic housing, or shields as they are sometimes called, add structure and support to make the crimp more durable. The plastic housings come in various sizes that can hold multiple connections in one block. Some projects will have all the connections next to each other which make the multi-connection block very convenient to use. Using single pin housing is easier to learn on and creates wires that have more flexibility in how they can be connected.
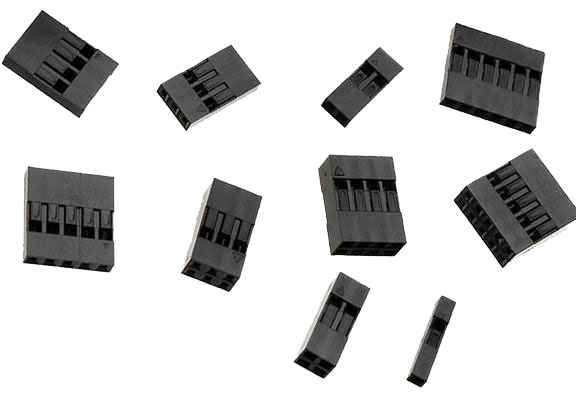

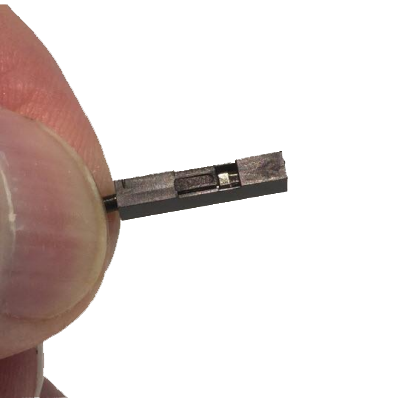
Both the male and female header pins have a small square or rectangle of metal in the pin mating zone. This metal “tab” will lock itself into the square opening or “slot” in the housing. Make sure the tab and the slot are facing the same direction and push the crimp into the larger opening in the housing. If done successfully the crimp will lock itself in the housing.

Perform a pull test to confirm that the crimp will not slip out of the housing. If the housing does not easly slip off you have successfully made a crimp!

Cut enough of the conduit to fit the majority of the wiring. Push the wire inside the conduit until it is all the way through. You may want to leave part of the white wire out of the conduit to allow it to reach the other side of the arduino.

Attach the newly created wires to the Distance Sensor. You will need to attach the female header pin of the black wire to the GND port of the Distance Sensor, the female header pin of the red wire to the 5V port of the Distance Sensor, and the female header pin of the white wire to the SIG port of the Distance Sensor.
Using the wiring diagram connect the distance sensor to the arduino.

What happens?

You now have your wires contained inside the flexible conduit that connects the Distance Sensor to your Arduino. The ends should have the proper header pins connected. This is what a typical wiring harness would consist of: The wires you would need to connect the components together, and the header pins or connectors that are needed to plug the connectors together.

